Predicting clinical outcomes from preclinical data is essential for identifying safe and effective drug combinations. Current models rely on structural or target-based features to identify high-efficacy, low-toxicity drug combinations. However, these approaches fail to incorporate the multimodal data necessary for accurate, clinically-relevant predictions.
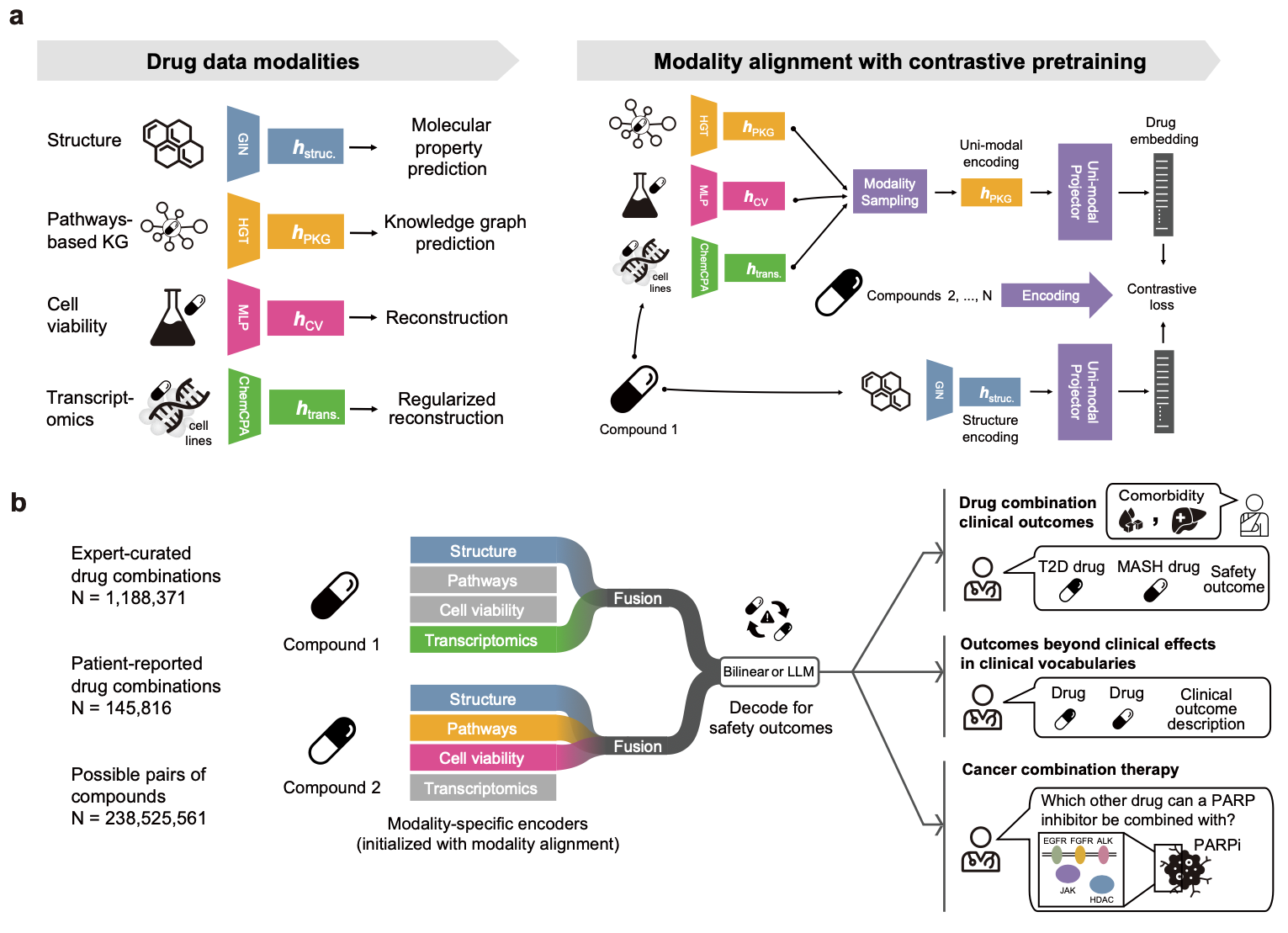
Here, we introduce MADRIGAL, a multimodal AI model that learns from structural, pathway, cell viability, and transcriptomic data to predict drug combination effects across 953 clinical outcomes and 21842 compounds, including combinations of approved drugs and novel compounds in development. MADRIGAL uses a transformer bottleneck module to unify preclinical drug data modalities while handling missing data during training and inference--a major challenge in multimodal learning.
It outperforms single-modality methods and state-of-the-art models in predicting adverse drug interactions. MADRIGAL performs virtual screening of anticancer drug combinations and supports polypharmacy management for type II diabetes and metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH). It identifies transporter-mediated drug interactions. MADRIGAL predicts resmetirom, the first and only FDA-approved drug for MASH, among therapies with the most favorable safety profile. It supports personalized cancer therapy by integrating genomic profiles from cancer patients. Using primary acute myeloid leukemia samples and patient-derived xenograft models, it predicts the efficacy of personalized drug combinations. Integrating MADRIGAL with a large language model allows users to describe clinical outcomes in natural language, improving safety assessment by identifying potential adverse interactions and toxicity risks. MADRIGAL provides a multimodal approach for designing combination therapies with improved predictive accuracy and clinical relevance.
Publication
Multimodal AI predicts clinical outcomes of drug combinations from preclinical data
Yepeng Huang, Xiaorui Su, Varun Ullanat, Ivy Liang, Lindsay Clegg, Damilola Olabode, Nicholas Ho, Bino John, Megan Gibbs, Marinka Zitnik
In Review 2025 [arXiv]
@article{huang2025madrigal,
title={Multimodal AI predicts clinical outcomes of drug combinations from preclinical data},
author={Huang, Yepeng and Su, Xiaorui and Ullanat, Varun and Liang, Ivy and Clegg, Lindsay and Olabode, Damilola and Ho, Nicholas and John, Bino and Gibbs, Megan and Zitnik, Marinka},
journal={arXiv:2503.02781},
url={https://arxiv.org/abs/2503.02781},
year={2025}
}
Code and Data Availability
Pytorch implementation of PocketGen is available in the GitHub repository. Datasets are also available at Harvard Dataverse repository.