Graph unlearning, which involves deleting graph elements such as nodes, node labels, and relationships from a trained graph neural network (GNN) model, is crucial for real-world applications where data elements may become irrelevant, inaccurate, or privacy-sensitive.
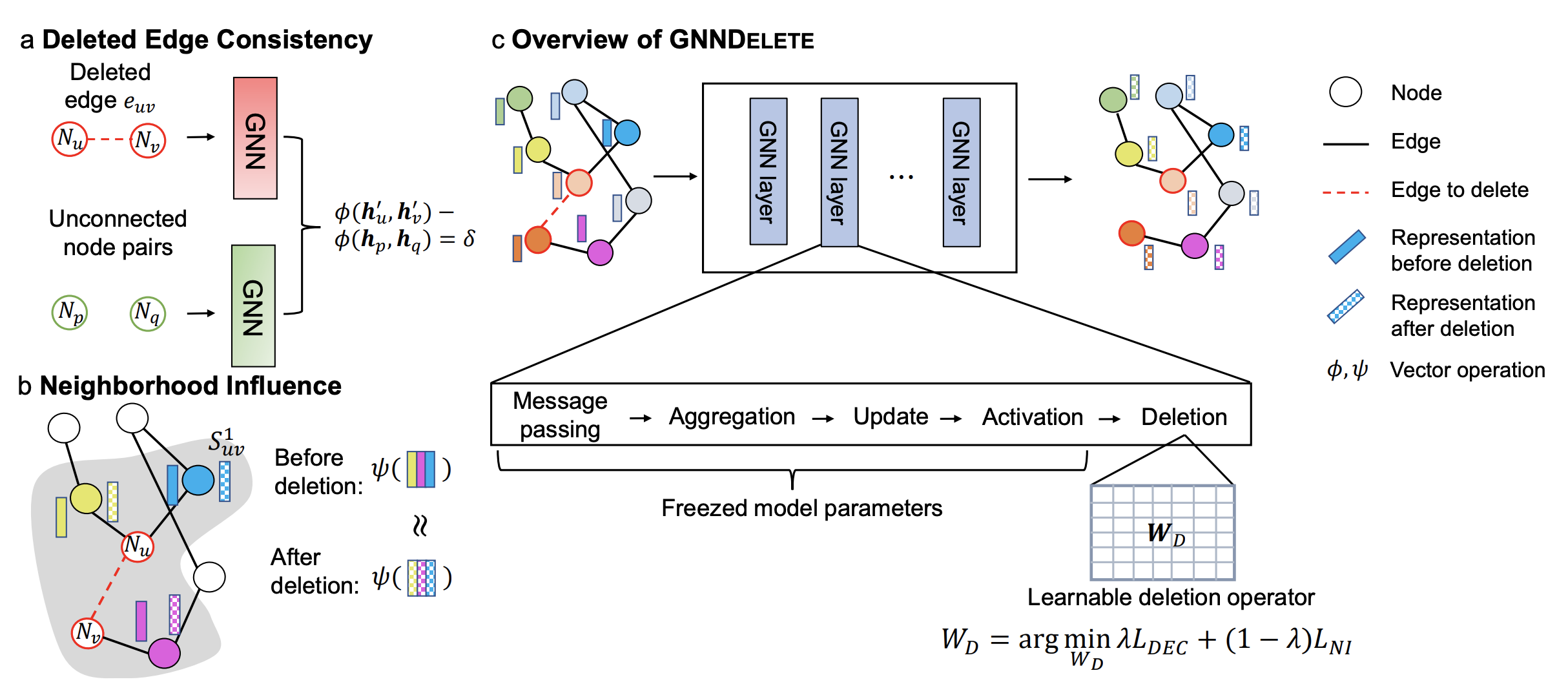
However, existing methods for graph unlearning either deteriorate model weights shared across all nodes or fail to effectively delete edges due to their strong dependence on local graph neighborhoods. To address these limitations, we introduce GNNDelete, a novel model-agnostic layer-wise operator that optimizes two critical properties, namely, Deleted Edge Consistency and Neighborhood Influence, for graph unlearning. Deleted Edge Consistency ensures that the influence of deleted elements is removed from both model weights and neighboring representations, while Neighborhood Influence guarantees that the remaining model knowledge is preserved after deletion.
GNNDelete updates representations to delete nodes and edges from the model while retaining the rest of the learned knowledge. We conduct experiments on seven real-world graphs, showing that GNNDelete outperforms existing approaches by up to 38.8% (AUC) on edge, node, and node feature deletion tasks, and 32.2% on distinguishing deleted edges from non-deleted ones. Additionally, GNNDelete is efficient, taking 12.3x less time and 9.3x less space than retraining GNN from scratch on a large knowledge graph.
Graph neural networks are being increasingly used in a variety of real-world applications, with the underlying graphs often evolving over time. Machine learning approaches typically involve offline training of a model on a complete training dataset, which is then used for inference without further updates. In contrast, online training methods allow for the model to be updated using new data points as they become available. However, neither offline nor online learning approaches can address the problem of data deletion, which involves removing the influence of a data point from a trained model without sacrificing model performance. When data needs to be deleted from a model, the model must be updated accordingly. In the face of evolving datasets and growing demands for privacy, GNNs must therefore not only generalize to new tasks and graphs but also be capable of effectively handling information deletion for graph elements from a trained model.
Background
Despite the development of methods for machine unlearning, none of these approaches are applicable to GNNs due to fundamental differences arising from the dependencies between nodes connected by edges (which we show in this paper). Existing machine unlearning methods are unsuitable for data with underlying geometric and relational structure, as graph elements can exert a strong influence on other elements in their immediate vicinity.
Furthermore, since the effectiveness of GNN models is based on the exchange of information across local graph neighborhoods, an adversarial agent can easily infer the presence of a data point from its neighbors if the impact of the data point on its local neighborhood is not limited. Given the wide range of GNN applications and the lack of graph unlearning methods, there is a pressing need to develop algorithms that enable GNN models to unlearn previously learned information. This would ensure that inaccurate, outdated, or privacy-concerned graph elements are no longer used by the model, thereby preventing security concerns and performance degradation. In this paper, we take a step towards building an efficient and general-purpose graph unlearning method for GNNs.
Designing graph unlearning methods is a challenging task. Merely removing data is insufficient to comply with recent demands for increased data privacy because models trained on the original data may still contain information about removed features. A naive approach is to delete the data and retrain a model from scratch, but this can be prohibitively expensive, especially in large datasets. Recently, efforts have been made to achieve efficient unlearning based on exact unlearning.
The core idea is to retrain several independent models by dividing a dataset into separate shards and then aggregating their predictions during inference. Such methods guarantee the removal of all information associated with the deleted data. However, in the context of GNNs, dividing graphs destroys the structure of the input graph, leading to poor performance on node-, edge- and graph-level tasks. To address this issue, uses a graph partitioning method to preserve graph structural information and aggregates predictions across individually retrained shards to produce predictions.
However, this approach is still less efficient as the cost increases as the number of shards grows. In addition, choosing the optimal number of shards is still unresolved and may require extra hyperparameter tuning. Several approximation-based approaches avoid retraining a model from scratch on data subsets. While these approaches have shown promise, these unlearning methods change the underlying predictive model in a way that can harm model performance.
GNNDelete: A General Strategy for Unlearning in GNNs
We introduce GNNDelete, a general approach for graph unlearning that can delete nodes, node labels, and relationships from any trained GNN model. We formalize two essential properties that GNN deletion methods should satisfy:
1) Deleted Edge Consistency: predicted probabilities for deleted edges in the unlearned model should be similar to those for nonexistent edges. This property enforces GNNDelete to unlearn information such that deleted edges appear as unconnected nodes.
2) Neighborhood Influence: we establish a connection between graph unlearning and Granger causality to ensure that predictions in the local vicinity of the deletion maintain their original performance and are not affected by the deletion. However, existing graph unlearning methods do not consider this essential property, meaning they do not consider the influence of local connectivity, which can lead to sub-optimal deletion.
To achieve both efficiency and scalability, GNNDelete uses a layer-wise deletion operator to revise a trained GNN model. When receiving deletion requests, GNNDelete freezes the model weights and learns additional small weight matrices that are shared across nodes in the graph. Unlike methods that attempt to retrain several small models from scratch or directly update model weights, which can be inefficient and suboptimal, GNNDelete learns small matrices for inference without changing GNN model weights. To optimize GNNDelete, we specify a novel objective function that satisfies Deleted Edge Consistency and Neighborhood Influence and achieves strong deletion performance.
Our Contributions
We present our contributions as follows:
- We introduce GNNDelete, a novel deletion operator that is both flexible and easy-to-use, and can be applied to any GNN model. We also introduce two fundamental properties that define effective unlearning on graph data.
- The difference between node representations returned the baseline GNN model and those revised by GNNDelete is theoretically bounded, ensuring the strong performance of GNNDelete.
- We evaluate GNNDelete across a wide range of deletion tasks including edge deletion, node deletion, and node feature unlearning, and demonstrate that it outperforms existing graph unlearning models. Our experiments show that GNNDelete performs consistently well across a variety of tasks and is easy to use. Results demonstrate the potential of GNNDelete as a general strategy for graph unlearning.
Publication
GNNDelete: A General Strategy for Unlearning in Graph Neural Networks
Jiali Cheng, George Dasoulas, Huan He, Chirag Agarwal, Marinka Zitnik
International Conference on Learning Representations, ICLR 2023 [Slides]
@inproceedings{cheng2023gnndelete,
title = {GNNDelete: A General Strategy for Unlearning in Graph Neural Networks},
author = {Cheng, Jiali and Dasoulas, George and He, Huan and Agarwal, Chirag and Zitnik, Marinka},
booktitle = {International Conference on Learning Representations, ICLR},
year = {2023}
}
Code
PyTorch implementation together with documentation and examples of usage is available in the GitHub repository.